1. Why do we need a networking model in the first place 🤔?
Networking models provide a defined structure for networking protocols and standards. This then helps to create a common and efficient way to understand the flow of the network hence, creating a larger community to approach when you get stuck.
In short, it's just a set of rules saying how the network devices should work.
Now, the reason we need standardization in networks is that without it every company/manufacturer would introduce their own networking protocol exclusively available to their products.
So no products from other companies would be able to efficiently communicate with each other
2. The OSI Model ( Open Systems Interconnection ) 📦
- It was the first standard model for network communications, adopted by all major computer and telecommunication companies in the early 1980s
- Created by the ‘ International Organization for Standardization ’ (ISO).
- Functions are divided into 7 layers and together make a network work.
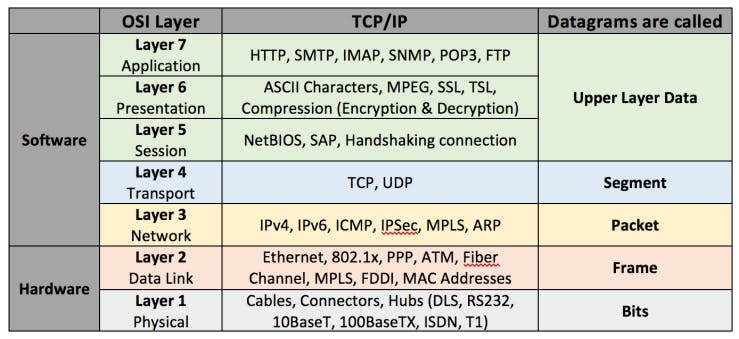
2.1 Layer 7 - Application Layer
- Data here is in application format.
- This Layer is closest to the end user
- This layer interacts with your web browsers like chrome, edge ..etc
- HTTP ( port number 443 ) and HTTPS ( port number 80 ) are layer 7 protocols.
- Functions of this layer are to identify communication partners and synchronize communications.
2.2 Layer 6 - Presentation Layer
- The application formatted data needs to be translated to a different format to send it over the network.
- This job is done by the Presentation Layer.
- for example, encryption of data as it is sent, and decryption of data as it is received.
2.3 Layer 5 - Session Layer
- This layer controls the session between the communicating hosts.
- This layer establishes, manages, or terminates connections between the applications.
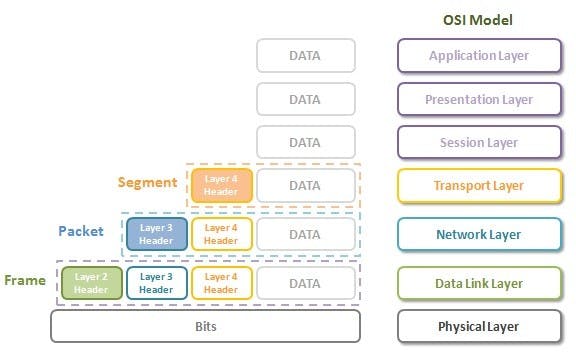
2.4 Layer 4 - Transport Layer
- The packet data unit in this layer is called segment.
- A larger chunk of data is broken down into segments that can easily travel over the network when sending data and are reassembles visa versa.
- Examples of this layer are TCP and UDP - which provide host-to-host communication.
2.5 Layer 3 - Network Layer
- The Packet data unit in this layer is called packets.
- Provides connectivity between different networks.
- Provides IP addressing.
- Provides path selection between source and destination.
- Routers operate at layer 3.
2.6 Layer 2 - Data Link Layer
- The packet data unit in this layer is called frame.
- Defines how data is formatted for transmission over the physical network.
- Uses Layer 2 addressing i.e. mac addressing ..etc.
- Switches operate at layer 2.
2.7 Layer 1 - Physical Layer
- The packet data unit in this layer is called bit.
- Defines physical characteristics of the medium used to transfer data between devices.
- Digital bits are converted into electrical (for wired connections) or radio (for wireless connections) signals.
TCP / IP suite 📦
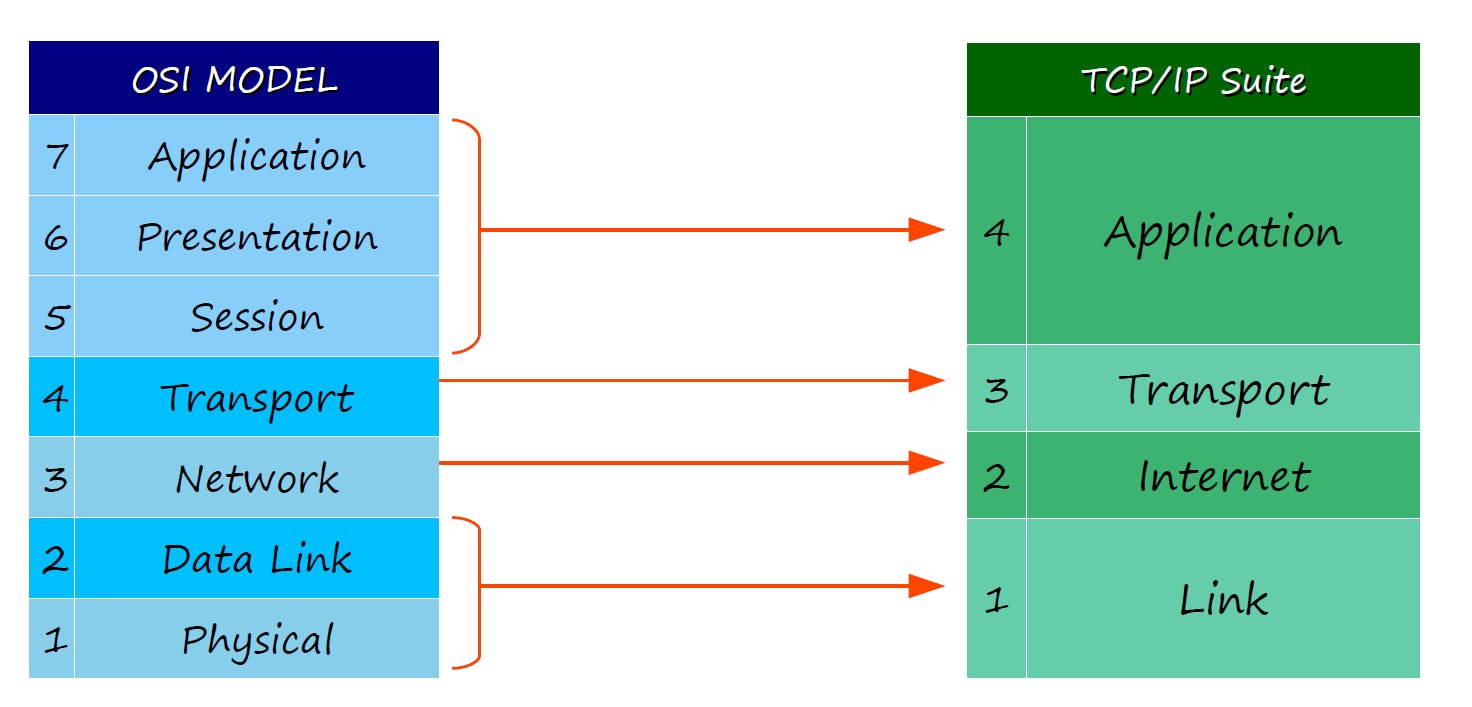
- Developed by the United States Department of Defense through DARPA (Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency)
- Similar structure to the OSI Model, but with fewer layers.
- This is the model actually in use in modern networks.
